Overview
Does a septate uterus cause recurrent miscarriage? A septate uterus is responsible for many recurrent early and late miscarriages. An estimate of up to 40 percent of women with uterine septum goes through recurrent miscarriage.
So, what is a septate uterus? It is a malformation of the uterus, otherwise known as uterus anomaly. Uterus anomalies are a congenital condition that women are born with, and the septate uterus is the most common type of anomalies. A septate uterus is where the septum divides the uterus partially or completely.
Symptoms Of A Septate Uterus
A septate uterus is usually asymptomatic, and it does not necessarily lead to fertility or pregnancy issues. However, the dividing septum mainly comprises fibrous band of tissue, which obstructs blood circulation. As a result, it can easily lead to miscarriage, infertility, premature birth, or abnormal fetal position.
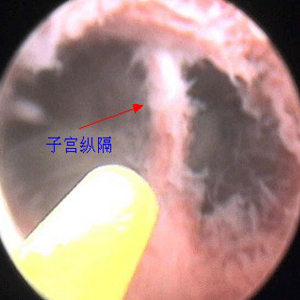
Diagnosis Of A Septate Uterus
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG). The X-ray examination of fallopian tubes and uterus is one of the most used methods of diagnosis.
- 4D Color Doppler Ultrasound. The results will be more accurate if the ultrasound is done before menstruation.
- Diagnostic digital Hysteroscopy. Hysteroscopy is the most direct and accurate in determining the type of uterine anomaly. It can also check if the septate is partial or complete. Hysteroscopy should be done routinely before proceeding with the septum removal surgery.
The Conventional Method Of Treating A Septate Uterus
Before the existence of operative hysteroscopy, surgeons performed abdominal surgery to remove the septate. The surgeons would either remove the septate by making an incision on:
- The fundus (uppermost curved portion) of the uterus, or
- The body (middle) of the uterus
After removal of the septate, the muscle wall of the uterus would be reconstructed. However, this method creates large surgical scars and requires a long recovery time. It might even lead to intrauterine adhesions (Asherman’s syndrome), where scar tissues are formed between the uterus’ inner walls. As a result, some must wait a few years before getting pregnant and can only give birth through a cesarean delivery. Currently, many hospitals remove the septate through operative hysteroscopy. However, the possibility of intrauterine adhesions after the surgery still exists, which might even lead to infertility.
Antai Hospital Treatment
Antai hospital uses both hysteroscopy and laparoscopy to remove the dividing septum. The conventional cold knife surgical technique is used rather than electrosurgical instruments. Cold knife surgical technique will significantly reduce scarring as compared to using the electrosurgical instruments. Before closing the incision site, the surgeons will place an adhesion barrier to reduce internal scarring further and insert an intrauterine balloon stent into the cavity of the uterus. On the seventh day, the surgeons will remove the intrauterine balloon stent. At the same time, the tissue surfaces will heal, and the adhesion barrier will dissolve. Three months after the surgery, patients can conceive naturally.
To Conclude
Although women with a septate uterus will face a high risk of miscarriage, it is still possible to have normal pregnancies even with this condition. At Antai hospital, the treatment for septate uterus reduces the likelihood of scarring and preventing intrauterine adhesions. Many women also manage to conceived and give birth to healthy babies successfully.
However, if you have experienced recurrent miscarriage, it is advisable to receive a thorough and in-depth diagnosis. Miscarriages can be emotionally and physically traumatizing. It is essential to do a complete body check before getting pregnant again. Antai hospital is a service-centric maternity hospital specializing in recurrent miscarriage with a 95 percent success rate. At Antai Hospital, we care for your well-being. It is our priority to provide accurate diagnosis and effective treatment for our patients.