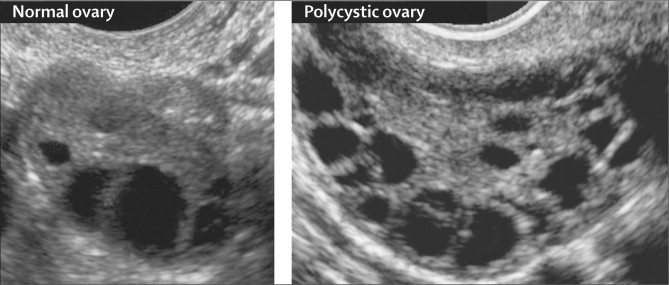
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is currently the leading cause of menstrual complications in women. It is characterized by clinical and/or biochemical hyperandrogenism, ovulation abnormalities and the presence of enlarged and/or polycystic ovaries in ultrasound images (12 or more small bubbles located circumferentially and/or ovarian volume > 10 mL). It is often comorbid with hyperinsulinemia, dyslipidemia, overweight or obesity, and is a risk factor for the development of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). The treatment of patients with PCOS depends on the prevailing symptoms.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), also known as the Stein-Leventhal syndrome, is one of the most common endocrinopathies among women of reproductive age. It is estimated that it affects 3–15% of all women. An abnormality in the ovaries is the primary cause of the disorder, but additional agents, such as obesity and environmental factors, affect the development of individual symptoms. Specifically, there is an abnormal trace amount of leftover testicular tissue that have not completely degenerated, causing a defect in ovarian cells leading to androgen secretion. How women develop these ovarian abnormalities maybe caused by several undetermined factors but it is indeed classified as a congenital condition. The Rotterdam criteria are the most widely used and relevant criteria for the diagnosis of PCOS. The disorder is diagnosed if 2 of the 3 specified conditions are met: hyperandrogenism (detected by clinical and/or biochemical testing) (2) ovulation abnormalities, and/or 12 or more cysts on one ovary and/or ovarian volume > 10 mL. There are also 2 other definitions of the syndrome in addition to the Rotterdam criteria. According to the criteria proposed by the National Institutes of Health (NIH, 2009), a diagnosis of PCOS involves detection of clinical or biochemical hyperandrogenism and chronic ovulation disorders. The Androgen Excess Society (2006), on the other hand, treats hyperandrogenism as the basic PCOS disorder and the prerequisite for a diagnosis, in combination with one of the 2 remaining Rotterdam criteria.
Symptoms
- Obesity
- Insulin resistance
- Dark patchy skin
- Excessive hair growth
- Rougher voice
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Infrequent periods
- Infertility
Diagnosis
At Antai, we conduct 4 primary tests to diagnose PCOS:
- Ultrasound to visualize the ovaries
- Blood profiling
- Understanding your cycle
- Observation of physical symptoms by our doctors
Treatment
At Antai Hospital, we know that PCOS is caused the abnormal presence of these testicular tissues that are responsible for the excessive androgen and also the culmination of this disease. Accurately removing them from the ovaries while maintaining organ function is done via 3D – Laparoscopy. This treatment is much more reliable and effective than reliance on medication or herbs, and can even guarantee pregnancy afterwards.